CDN network is a content distribution network. Large websites, especially live broadcast and video platforms, generally use CDN acceleration technology. Its principle is similar to that of JD Logistics, which uses local warehouses to accelerate logistics efficiency. This article explains it well.
----------Body----------
Nowadays, in the era of mobile Internet, more and more people use mobile phones to watch videos and enrich their entertainment life.
However, have you ever thought about one question when you are chasing the show - why do you sometimes get stuck when watching videos even though your mobile phone's Internet speed is very fast?
Before answering this question, let's do an arithmetic problem.
Take the previously popular "Yanxi Strategy" as an example. At that time, 10 million users were able to watch a video app online at the same time.
If you watch 1080p video (theoretically, 4Mbps bandwidth is required), then the cumulative traffic bandwidth required is 10000000 × 4Mbps=40000000Mbps=40Tbps.
For Internet video content providers like Youku and iQiyi, this is undoubtedly a huge traffic pressure.
The network card of our ordinary computer is 1Gbps bandwidth. If Youku has a super server, this super server needs 40000 network cards , and it must run at 100% full speed to achieve the smooth viewing of the 10 million users.
For some service providers with insufficient strength, or sudden traffic increases sharply, congestion will result, which will lead to stuck and delay.
There is a saying that when a user opens a page and waits for more than 4 seconds, he will close the page. In other words, the user will be lost.
▼ This should be the most annoying symbol
The loss of users means the loss of money. No Internet service provider wants this to happen. Therefore, they must find ways to make their content present as soon as possible, shorten the waiting time of users, and improve the user experience.
CDN is a very effective Shorten delay Technology.
Birth of CDN
In the 1980s, Internet technology just entered the civil field.
People access the network mainly through dial-up, with low bandwidth and few users, so there is no pressure on the backbone network and servers.
With the explosive development of the Internet, there are more and more users. In addition to the emergence of broadband access networks, the pressure on content source servers and backbone networks is growing, and they cannot respond to users' access needs in a timely manner.
In 1995, professor of Massachusetts Institute of Technology, one of the inventors of the Internet, Tim Berners-Lee Doctor found that network congestion is becoming more and more serious, which will become the biggest obstacle to the development of the Internet.

Tim Berners-Lee
Therefore, he proposed an academic problem, hoping that someone could invent a new and fundamental solution to the problem to achieve congestion free distribution of Internet content.
Next to Dr. Tim Berners Lee Tom Leighton The professor's office. He is a professor of applied mathematics at MIT.

Tom Leighton
He was intrigued by Berners Lee's challenge, so he invited graduate students Danny C. Lewin Work with several other top researchers to solve this technical problem.

Danny C. Lewin
Finally, they developed a dynamic routing algorithm technology that uses mathematical algorithms to process content, effectively solving this problem. This technology is called CDN.
They also set up a company specifically for this purpose to give full play to its commercial value. This company is the originator of the later famous CDN service—— Akamai 。
Principle of CDN
In fact, CDN is not complicated. The original core idea is Cache content near end users 。
Isn't the content source far away? So, we will build a cache server near the user, copy the remote content, and put it here. Is that OK?
Because this technology distributes content, its name is CDN—— Content Delivery Network 。
Specifically, CDN is to use more cache servers (CDN edge nodes) and deploy them in areas or networks where users have relatively concentrated access. When a user visits a website, the global load technology is used to point the user's access to the nearest cache server, and the cache server responds to the user's request. (Is it a bit like the local warehouse of e-commerce?)
You may think that this is Mirror Server What? Actually, it is different. The mirror server is a full copy of the source content server. CDN is a cache of some content, which is more intelligent.
Specifically, CDN=more intelligent image+cache+traffic diversion 。
It should also be noted that CDN can not only cache video content, but also distribute static resources of websites (such as various types of pictures, html, css, js, etc.), and static content of mobile app apps (such as installation package apk files, pictures and videos in apps, etc.).
Let's take an example to see the details of CDN Workflow 。
If a user wants to access Youku's video on demand content, then:
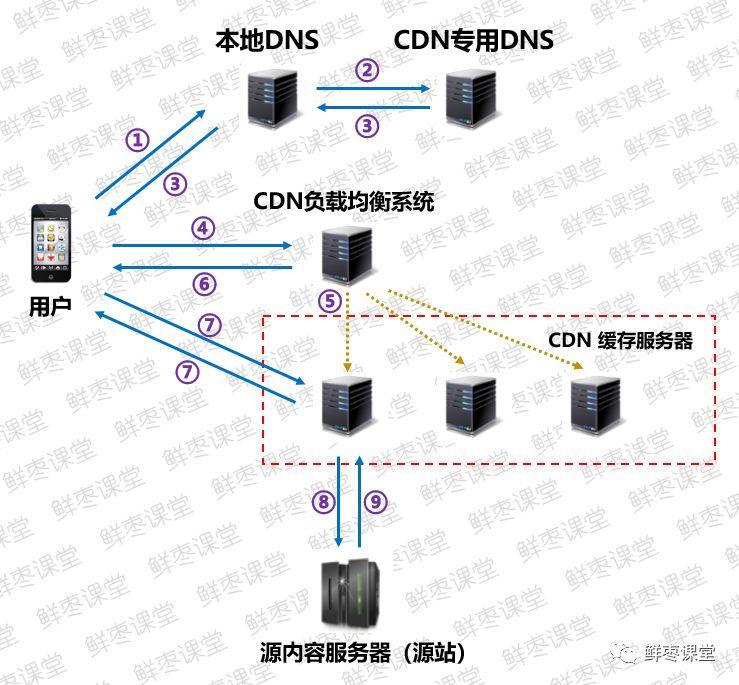
Specific steps:
① When the user clicks the content on the APP, the APP will go to Local DNS (Domain name resolution system) Seek IP address resolution.
② The local DNS system will give the domain name resolution right to CDN dedicated DNS server 。
③ The CDN dedicated DNS server returns the IP address of the CDN global load balancing device to the user.
④ , users to CDN load balancing device Initiate a content URL access request.
⑤ The CDN load balancing device selects a user's IP address and the content URL requested by the user Cache server 。
⑥ The load balancing device tells the user the IP address of the cache server, and lets the user send a request to the selected cache server.
⑦ The user sends a request to the cache server, which responds to the user's request and transmits the content required by the user to the user terminal.
⑧ . If the cache server does not contain the content the user wants, the cache server will Source Server Request content.
⑨ The source server returns the content to the cache server, which sends it to the user, and judges whether to cache the content to the cache server according to the user-defined cache policy.
CDN Benefits
The biggest advantage of using CDN technology is that it speeds up website access - the physical distance between users and content is shortened, and the waiting time of users is also shortened.
In addition, cache servers distributed to different lines also accelerate access across operators.
For example, China Mobile mobile phone users can speed up their access to the content source of China Telecom network by setting up CDN servers in China Mobile. The effect is very obvious.
In addition, CDN has security benefits. After the content is distributed, the IP address of the source server is hidden, and the probability of being attacked will be greatly reduced. In addition, when a server fails, the system will call nearby health servers for services to avoid affecting users.
Because of the many benefits of CDN, all mainstream Internet service providers have adopted CDN technology. All cloud service providers also provide CDN services (the price is not expensive, and they are charged by traffic).
CDN service of XX cloud
CDN and communication industry
CDN is a service developed from the traditional IT industry. However, CDN also has great commercial value for our communications industry.
Internet service provider adopts CDN, which is Exchange storage for delay 。 Spend money to purchase CDN servers or cloud computing services in exchange for a better user experience.
Communication operators also pursue CDN, but their purpose is Exchange storage for bandwidth ——Through the "sinking" of services, the traffic pressure of the upper backbone network is reduced, hardware expansion is avoided, and network construction costs are reduced.
This is easy to understand. If a large amount of traffic data is running around the backbone network, the backbone network will not be able to afford it, and will try to expand its capacity. If these traffic data are solved at the bottom, the bandwidth pressure of the backbone network will naturally be reduced. Isn't it?
Many operators have sunk CDN to the municipal level to reduce pressure and improve user experience.
Speaking of this, have you thought of anything?
Yes, this is the same as the one introduced a few days ago Move Edge Calculation There are similarities and differences.
For a long time, with the continuous improvement of network capabilities, content resources and computing capabilities are constantly "going up" to the cloud computing center. A core cloud computing center provides services to all terminal nodes.

As a result, people look back and find that for a very large area, a very large number of users, especially national or world-class services, no matter where the center is located or how powerful the center is, it cannot be overcome Obstacles in physical distance , will lead to unbearable delayed and network congestion 。
As a result, people began to partially "sink" the cloud computing center, which led to fog computing and haze computing. Even people began to question, Will centralized computing eventually be replaced by distributed computing?

Blockchain is the representative of distributed computing
In Xiao Zao Jun's opinion, there is no question of who will completely replace whom. Different scenarios bring different requirements, and different requirements require different network architectures. The diversity of scenarios exists in reality, so the flexibility of network architecture is also an inevitable choice.
The upcoming 5G, which proposes three scenarios and slices, uses the same network to meet different needs, reflects this design idea and conforms to the trend of development.
In a word, for network technology, whether it is black or white, in a word, good cats are the ones who can catch mice. Isn't it?
